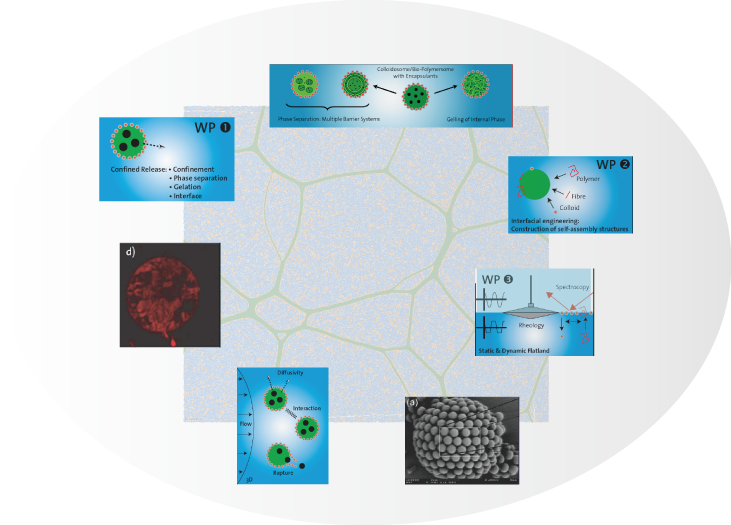
New controlled release systems produced by self-assembly of biopolymers and colloidal particles at fluid-fluid interfaces
| We have synthesized a new amphiphilic block oligomer by the enzymatic linking of a fatty acid (lauric acid) to a fructan oligomer (inulin) and tested the functionality of this carbohydrate derivative in foam stabilization. The structure of the modified oligosaccharide was found to be (Fruc)(n)(Glc)(1)CO-C11H23, which implies that on average one lauric acid molecule was linked to one inulin molecule. The new component produces foams with exceptional stability. Our results show that enzymatic acylation can produce an entirely new class of amphiphilic materials, with functionality comparable to that of synthetic block copolymers. [hide]
Scientific Board
Scientific Stuff
Associated Scientists |
|
Enjoy your reading
SY Tee, AR Bausch, PA Janmey, | |
Selected conferences (co-)organized by project members8th World Congress on Computational Mechanics WCCM8 200830 June - 5 July 2007, Venice, Italy ► |
13 May 2025
![]() mk
mk