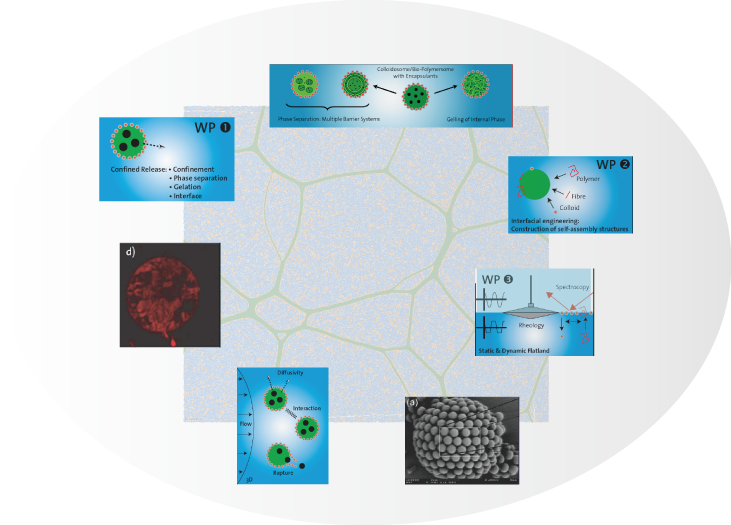
New controlled release systems produced by self-assembly of biopolymers and colloidal particles at fluid-fluid interfaces
| The structural organization of the cytoskeleton determines its viscoleastic response which is crucial for the correct functionality of living cells. Both the mechanical response and microstructure of the cytoskeleton are regulated on a microscopic level by the local activation of different actin binding and/or bunding proteins (ABPS). Misregulations in the expression of these ABPs or mutations in their sequence can entail severe cellular dysfunctions and disease. Here, we study the structural and viscoelastic properties of reconstituted actin networks cross-linked by the ABP espin and compare the obtained network properties to those of other bundled actin networks. Moreover, we quantify the impact of pathologically relevant espin mutation on the viscoelastic properties of these cytoskeletal networks. [hide]
Scientific Board
Scientific Stuff
Associated Scientists |
|
Enjoy your reading
SY Tee, AR Bausch, PA Janmey, | |
Selected conferences (co-)organized by project members8th World Congress on Computational Mechanics WCCM8 200830 June - 5 July 2007, Venice, Italy ► |
13 May 2025
![]() mk
mk