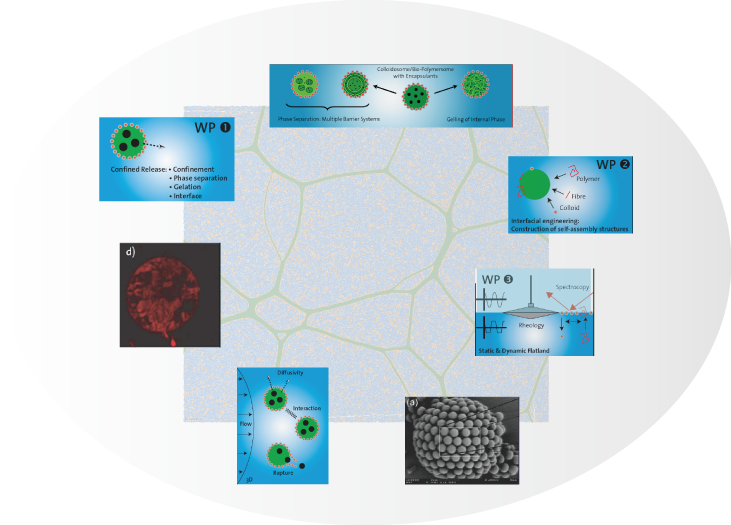
New controlled release systems produced by self-assembly of biopolymers and colloidal particles at fluid-fluid interfaces
| In contrast with entangled actin solutions, transiently cross-linked actin networks can provide highly elastic properties while still allowing for local rearrangements in the microstructure-on biological relevant time scales. Here, we show that thermal unbinding of transient cross-links entails local stress relaxation and energy dissipation in an intermediate elasticity dominated frequency regime. We quantify the viscoelastic response of an isotropically cross-linked actin network by experimentally tuning the off rate of the transiently cross-linking molecules, their density, and the solvent viscosity. We reproduce the measured frequency response by a semiphenomenological model that is predicated on microscopic unbinding events. [hide]
Scientific Board
Scientific Stuff
Associated Scientists |
|
Enjoy your reading
SY Tee, AR Bausch, PA Janmey, | |
Selected conferences (co-)organized by project members8th World Congress on Computational Mechanics WCCM8 200830 June - 5 July 2007, Venice, Italy ► |
13 May 2025
![]() mk
mk